How to stimulate biodiversity and the biological control of pests
Futurcrop - 18-02-2019
The effect of chemical insecticides against pests, and also against their natural predators, and the simplification of the agricultural landscape, indiscriminately eliminating weeds, the native flora and shrub as a reservoir of useful fauna, are some of the main causes of the problem of the current proliferation of pests in the Agriculture.
Agriculture considered as an industrial process of food production, which increases production at the lowest cost and accelerates processes through chemical products, has caused serious environmental problems for years. Among other things, this production system favors the cleaning of fields of bushes, hedges, trees and shrubs. But this practice supposes the reduction of biodiversity in the agricultural landscapes and the elimination of the proper habitats of the native species of predators and parasites of plagues, and causes therefore a greater vulnerability of the crops to pests and diseases.
This intensification in agricultural production creates a high pressure of pests and diseases on crops, which is usually controlled with chemicals insecticides. However, numerous investigations show that the indiscriminate use of agricultural insecticides causes damage to the environment, to the farmer´s health, and to the consumer himself through chemical residues in the crops. Knowing the damages that these products can cause, the usual practice of the systematic use of phytosanitary products in agriculture is justified exclusively by the economic benefit. The use of chemical insecticides should be limited to the imperative, and used when more efficient. And for this it is necessary to have a knowledge of the biological development of the plague, through frequent (or automated) monitoring and predictive software of the population dynamics of pests, such as FuturCrop.
Among the methods of combating the action of pests, it is increasingly common to use predators and parasites as alternative means to phytosanitary products. The pest biological control is usually understood as the introduction of the pests natural enemies (exotic in many times). But this type of biological control usually requires specialized technical assistance, knowledge of the state of biological development of the pest, and its success depends to a large extent on the appropriate climatological conditions for its release. The biological control of pests is also often an expensive resource compared to the application of insecticides.
But the biological control of pests can also be promoted in a natural, conservative way, introducting of certain modifications in the agricultural environment, the habitats, which favor the presence of natural and native enemies of pests. For example, thorough the introduction or preservation of multi-specific hedges (at least 5 shrub species), in the agricultural environment, shrubs, foliage, vegetation cover, weeds that do not affect the crop, islands of vegetation, green corridors, margins of fields with wild flowers, etc. that allows establishing a reservoir of predatory or parasitic species of pests, ensuring their habitat and their food. In this way, increasing the diversity of natural enemies reduces the density of the pest populations.
The management and conservation of semi-natural patches along the edges of roads, between plots, embankments and other unmanaged areas, helps to regulate phytophagous insect populations. Even weeds that do not interfere with the yield of the crop can provide food to insect populations throughout their life cycle, and are a fundamental support of animal biodiversity. It is important to control that the vegetable species for these habitats flourish sequentially, to provide food all year round (pollen or nectar) to the natural enemies of the pests, which are autochthonous vegetable species, and that non-species are host to viral diseases, which can be transmitted to crops.
In the Mediterranean environment, for example, the escobizo or white bowl is a plant that can serve in this sense and, in addition, it is a plant that contributes to the fertilization of the soil.
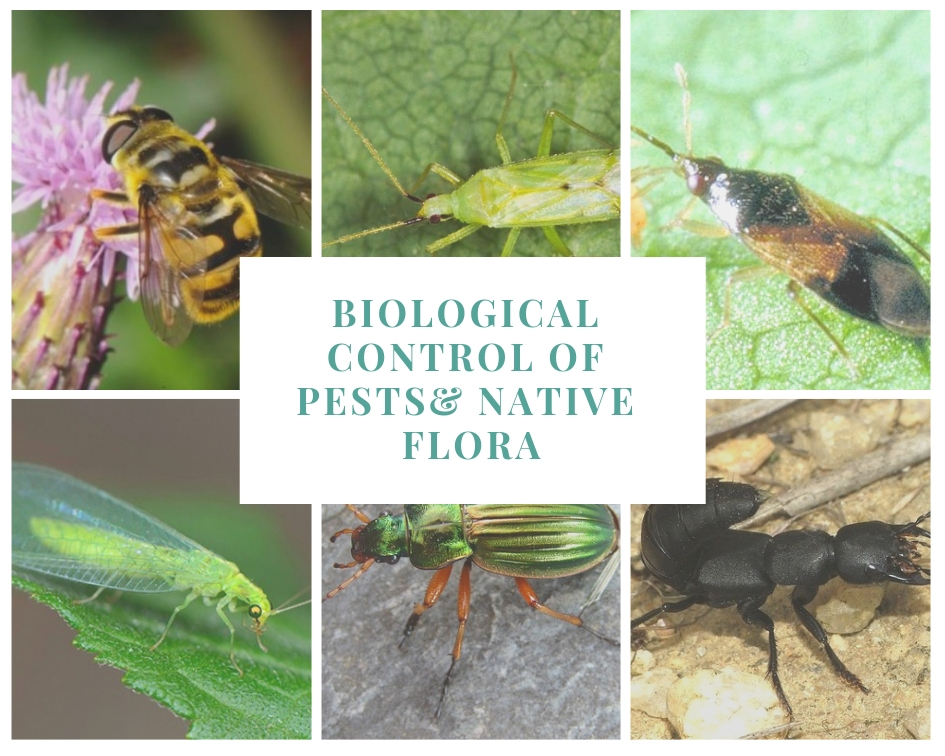
There are also other suitable plants that serve also as a reservoir of fauna, such anther, thyme, white esparraguera, rosemary, myrtle, esparto, etc. By conserving this type of habitats, we favor the presence of larvae and adults of the family of Carábidos (one of the largest families of the Coleoptera), present in hedges and cover crops, which are predators of caterpillars, pupae and adults of Lepidoptera. These plantas also increase the presence of staphylinids, which are Coleoptera predators of eggs and larvae of butterflies, or coccinellids, such as ladybugs, that prey both in adult and larval stages, aphids, mealybugs and other pest species. Bedbugs, which feed on aphids, eggs and other soft-bodied insects, such as Antocorides (which are usually found in flowers and prey on 20 to 40 mites and thrips daily), the Orius or the Myridae (for example, Dicyphus tamaninii and Macrolophus caliginosus, which contribute to the control of whitefly). The larvae of lacewings are aphid predators, although they also attack other agricultural pests, such as scales, psyllids, mites, etc. They are usually present in natural areas with presence of herbs, shrubs and trees, as they also feed on their nectar and pollen. Certain flies are predators of insects harmful to crops, such as those of the family of the Syrphids, which lay their eggs among the colonies of aphids to serve as food for their very voracious larvae. They also facilitate pollination when they are adults, as they feed on nectar and pollen.
Caribids
Lacewing
Staphylin
Miridos
Orius
Syrphids
Obviously this conservative biological control of pests, through the development and care of these habitats that facilitate the presence of native predators or parasitoids can have some drawbacks, since it reduces to some extent the surface of the agricultural areas, the habitats need some maintenance and can hinder the movement of machinery in the field. However, these disadvantages are compensated for by their beneficial effects, as it allows to reduce agricultural insecticides and increasing the resilience and productivity of crops.
Related Posts
How to reduce the use of chemical insecticides in the control of pests
FuturCrop improves the monitoring of pests and the effectiveness of treatments

Real time pest and vegetable diseases prediction models
Climatic Change and pest prevention technologies